IoT Remote Access: Benefits, Security & Management Tips
In an increasingly interconnected world, are you truly in control of your expansive network of IoT devices? The ability to remotely access and manage these devices is no longer a luxury, but a critical necessity for security, efficiency, and innovation.
The landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT) is vast and complex, encompassing everything from smart home appliances to sophisticated industrial sensors. These devices, while offering unprecedented convenience and data-driven insights, also present a significant challenge: how to effectively manage and secure them, especially when they are dispersed across diverse locations. The answer lies in robust remote access capabilities, enabling administrators to maintain vigilant oversight and respond swiftly to potential threats or operational anomalies.
| Category | Details |
| General Information | |
| Name | IoT Remote Access Solutions |
| Industry | Technology/Software |
| Headquarters | Global |
| Founded | Varies by provider |
| Services Offered | |
| Core Service | Remote IoT Device Management |
| Key Features | Secure Remote Access, Device Monitoring, Firmware Updates, Diagnostics, Automation |
| Target Audience | Enterprises, Small Businesses, Developers |
| Technology and Security | |
| Protocols Supported | SSH, VPN, HTTPS |
| Security Measures | Encryption, Multi-Factor Authentication, Access Control Lists |
| Device Compatibility | Linux, Raspberry Pi, Custom IoT Devices |
| Market Trends and Future | |
| Growth Factors | Increasing IoT Device Adoption, Growing Security Concerns |
| Future Trends | AI-powered Management, Edge Computing Integration, Enhanced Security |
| Reference Link | Example IoT Remote Access |
The importance of remote access to IoT devices cannot be overstated. In an age where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, the ability to address unauthorized activity before it escalates into significant damage is paramount. IoT remote access empowers administrators to swiftly identify, isolate, and mitigate potential security breaches, preventing data loss, system compromise, and reputational harm.
Beyond security, remote access unlocks a wealth of operational benefits. It facilitates proactive maintenance, allowing technicians to diagnose and resolve issues remotely, reducing downtime and minimizing the need for costly on-site visits. This is particularly crucial for IoT deployments in remote or difficult-to-access locations, such as oil rigs, wind farms, or transportation networks.
The benefits extend beyond mere troubleshooting. Remote access enables administrators to perform software updates, configure device settings, and monitor performance metrics from a centralized location. This streamlined management approach enhances efficiency, reduces operational costs, and ensures that IoT devices are operating at peak performance.
Moreover, the inherent wireless interconnectivity of IoT devices is amplified by remote access capabilities. It fosters seamless integration with other systems and platforms, enabling data sharing, automation, and real-time decision-making. This interconnectedness drives innovation, unlocks new business opportunities, and empowers organizations to leverage the full potential of their IoT investments.
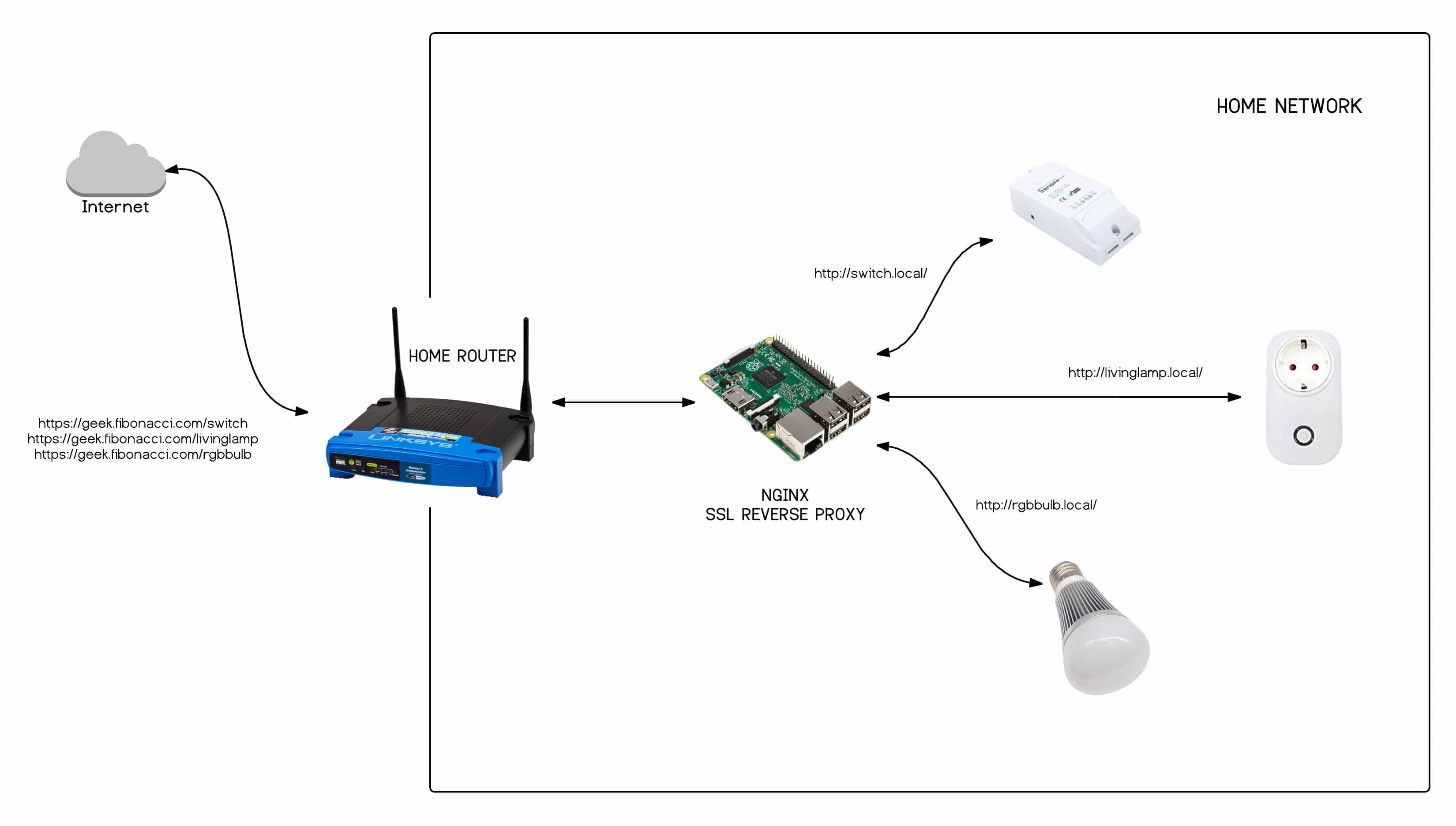
Several platforms are emerging to address the growing need for robust IoT device management and remote access. SocketXP, for instance, offers a cloud-based solution designed to simplify the complexities of managing distributed IoT deployments. These platforms provide a centralized interface for remotely managing, accessing, and monitoring IoT devices, Raspberry Pi fleets, and other Linux machines that reside behind NAT routers and firewalls.
The benefits of remote access for enterprises are particularly compelling in the realm of logistics. Consider the challenges of tracking and managing a fleet of connected vehicles or monitoring environmental conditions in remote warehouses. Remote access enables real-time visibility, proactive maintenance, and optimized resource allocation, leading to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
A recent study highlights the increasing adoption of IoT technology in the global supply chain market, projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2 percent between 2020 and 2030. This growth is fueled by the transformative potential of IoT to enhance visibility, optimize processes, and improve decision-making across the entire supply chain.
The supply chain divisions poised to benefit most from IoT technology include transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and demand forecasting. Remote access plays a crucial role in enabling these benefits, allowing organizations to monitor assets, track shipments, and optimize routes in real time, regardless of location.
However, the deployment of remote access solutions for IoT devices also presents certain challenges. One significant concern is the energy consumption of remote servers. Managing a large fleet of IoT devices remotely requires significant computing power, which can translate into substantial energy costs and environmental impact. Organizations must carefully consider the energy efficiency of their remote access solutions and explore options for reducing their carbon footprint.
So, how can you effectively manage your IoT devices remotely? Several key strategies can help businesses optimize their IoT device management practices:
1. Implement a Robust Security Framework: Prioritize security from the outset by implementing strong authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols, and access control lists. Regularly update software and firmware to patch vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats. Employ multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access, and conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential weaknesses.
2. Choose the Right Remote Access Solution: Select a remote access platform that aligns with your specific needs and technical capabilities. Consider factors such as scalability, security features, ease of use, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure. Evaluate cloud-based solutions, on-premises deployments, and hybrid approaches to determine the best fit for your organization.
3. Leverage Automation: Automate routine tasks such as software updates, configuration changes, and performance monitoring to reduce manual effort and improve efficiency. Implement automated alerts to notify administrators of critical events or anomalies, enabling proactive intervention and preventing potential problems from escalating.
4. Monitor Device Health and Performance: Continuously monitor the health and performance of your IoT devices to identify potential issues before they impact operations. Track key metrics such as CPU utilization, memory consumption, network latency, and device uptime. Implement predictive maintenance strategies to anticipate and prevent failures, minimizing downtime and maximizing device lifespan.
5. Establish Clear Policies and Procedures: Develop clear policies and procedures for managing and securing your IoT devices. Define roles and responsibilities for administrators, technicians, and end-users. Establish guidelines for password management, access control, and incident response. Regularly review and update these policies to reflect evolving threats and best practices.
Web applications can provide secure remote access to web applications running on IoT devices or machines on private networks. This allows users to interact with the devices' web interfaces from anywhere with an internet connection, providing a convenient way to monitor and control them remotely.
Another powerful technique for remote IoT access is using SSH (Secure Shell) over a VPN (Virtual Private Network). With a VPN configured and no VPN connection issues present, you can securely connect to your network and then access your IoT device through SSH as if you were on your local network. This approach offers a high level of security and control, making it suitable for sensitive applications.
Using SSH for remote IoT access offers numerous advantages, including:
Encryption: SSH encrypts all data transmitted between your device and the IoT device, protecting it from eavesdropping and interception.
Authentication: SSH uses strong authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of both the user and the device, preventing unauthorized access.
Port Forwarding: SSH allows you to forward ports from your local machine to the IoT device, enabling you to access services that are running on the device without exposing them directly to the internet.
Command-Line Interface: SSH provides a command-line interface that allows you to interact with the IoT device directly, giving you complete control over its configuration and operation.
Remote IoT platforms offer users the ability to remotely control IoT devices using a web browser. These platforms typically provide a user-friendly interface for managing devices, monitoring data, and executing commands. They can be particularly useful for non-technical users who need to interact with IoT devices without requiring specialized knowledge.
Finally, users can set up a VNC (Virtual Network Computing) server on a Raspberry Pi and use a VNC client application on a device of their choice to view and interact with the Pi's desktop from anywhere with an internet connection. This approach is particularly useful for graphical applications or when you need to interact with the Raspberry Pi's desktop environment.
In conclusion, the ability to remotely access and manage IoT devices is essential for organizations seeking to maximize the value of their IoT investments. By implementing robust security measures, choosing the right remote access solution, leveraging automation, and establishing clear policies and procedures, businesses can effectively manage their IoT deployments, mitigate risks, and unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Article Recommendations
- Onlyfans Insights Tips Tricks And 2023 Highlights
- Easy Guide Secure Remote Control Of Your Raspberry Pi

Detail Author:
- Name : Gail Witting
- Username : kessler.kristofer
- Email : elise.upton@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 2002-11-11
- Address : 688 Holly Passage Shieldsburgh, SD 44268-7416
- Phone : +12406562645
- Company : Quigley, Torp and Shields
- Job : Punching Machine Setters
- Bio : Atque deserunt molestiae non aliquid. Atque at natus veritatis rerum. Occaecati dicta quasi molestiae sed nesciunt eum. Error nisi quisquam et blanditiis reiciendis veritatis.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/devon153
- username : devon153
- bio : Et pariatur reiciendis quae et. Aperiam architecto est et et.
- followers : 4372
- following : 619
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/devon.crooks
- username : devon.crooks
- bio : Et voluptatibus labore eaque modi.
- followers : 5258
- following : 401