IoT Remote Control: Manage Devices From Anywhere [Explained]
Ever wondered if you could switch off your living room lights from a beach thousands of miles away? The answer is a resounding yes, thanks to the transformative power of remotely controllable IoT (Internet of Things) devices. This capability isn't just a futuristic fantasy; it's the reality that defines modern living and industrial operations, offering unparalleled convenience, efficiency, and control.
The Internet of Things has fundamentally reshaped how we interact with technology and the physical world. It has evolved from a theoretical concept to a tangible force that permeates every aspect of our lives. At its core, IoT involves embedding sensors, processing units, software, and diverse technologies into everyday physical objects. This interconnected web allows these devices to communicate, exchange data, and coordinate actions over the internet or other communication networks, effectively turning ordinary items into smart, responsive entities.
| Aspect | Information |
|---|---|
| Concept | Remote control and monitoring of IoT devices. |
| Key Technologies | Mobile apps, web portals, smart assistants, secure SSL/TLS VPN tunnels, cloud services. |
| Benefits | Enhanced user convenience, improved efficiency, remote diagnostics, proactive maintenance. |
| Examples | Smart thermostats, security cameras, industrial sensors, remote controlled machinery. |
| Cloud Platforms | Azure IoT Hub, Socketxp (cloud-based IoT remote access and device management). |
| Device Types | Raspberry Pi, Arduino, Nvidia Jetson, embedded Linux devices. |
| Communication Protocols | Internet, VPN, SSL/TLS. |
| Functionalities | Turning devices on/off, adjusting settings, monitoring performance, diagnosing issues, updating software. |
| Security Considerations | Secure communication channels, device authentication, data encryption, access control. |
| Reference | Azure IoT Hub |
The essence of IoT lies in its ability to create a network of interconnected devices that can communicate and share data without direct human intervention. This connectivity facilitates the automation of tasks, enhances decision-making processes, and enables predictive maintenance in various industries. From smart homes that regulate temperature and lighting to sophisticated industrial systems that monitor equipment performance and optimize energy consumption, IoT is transforming the way we live and work.
One of the most compelling features of IoT is the capacity for remote control and monitoring. This functionality allows users to interact with their devices from virtually anywhere in the world, provided they have an internet connection. Remote access to IoT devices empowers individuals to manage and control their environments, regardless of their physical location. This has profound implications for both personal convenience and operational efficiency.
Consider a scenario where you are on vacation and receive an alert that your home security system has detected unusual activity. With remote access, you can immediately view live video footage from your security cameras, activate the alarm system, and even contact local authorities. Similarly, in an industrial setting, engineers can remotely monitor the performance of critical equipment, diagnose potential issues, and initiate repairs before they escalate into costly breakdowns. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, optimizes resource allocation, and enhances overall productivity.
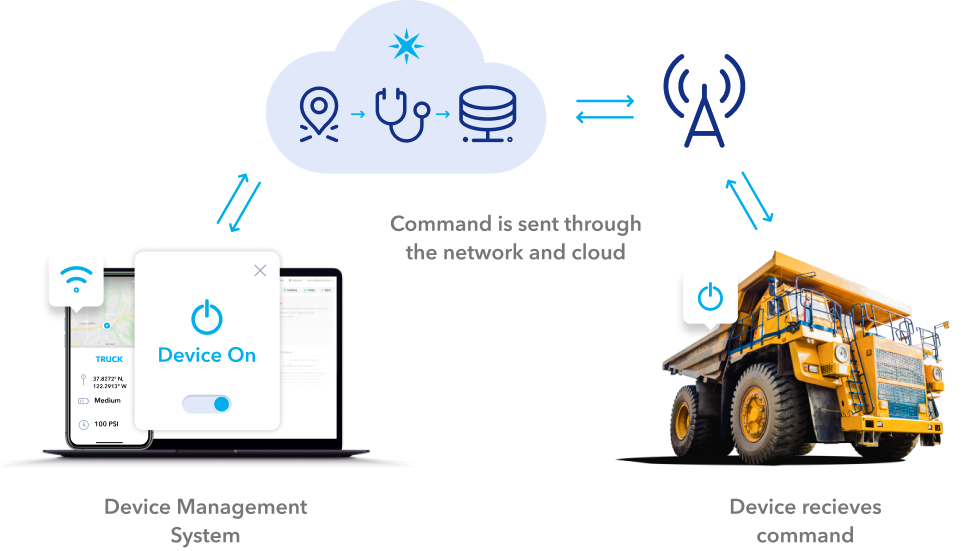
The mechanics of remotely controlling IoT devices involve a multi-layered approach. First, the device itself is equipped with sensors and processing capabilities that enable it to collect data and execute commands. This data is then transmitted over a network, typically the internet, to a central server or cloud platform. Users interact with the devices through a variety of interfaces, including mobile apps, web portals, and smart assistants. These interfaces send commands to the server, which in turn relays them to the targeted device. The device then executes the command and provides feedback to the user, confirming that the action has been completed.
- Aditi Mistry No Hot Videos Found Search Tips More
- Easy Remote Iot Access Over Internet Solutions Tools
Several technologies facilitate remote access and control of IoT devices. Mobile apps are perhaps the most common interface, offering a user-friendly way to manage devices from smartphones or tablets. Web portals provide a similar functionality through a web browser, allowing users to access their devices from any computer with an internet connection. Smart assistants, such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, offer voice-activated control, enabling users to manage their devices with simple voice commands.
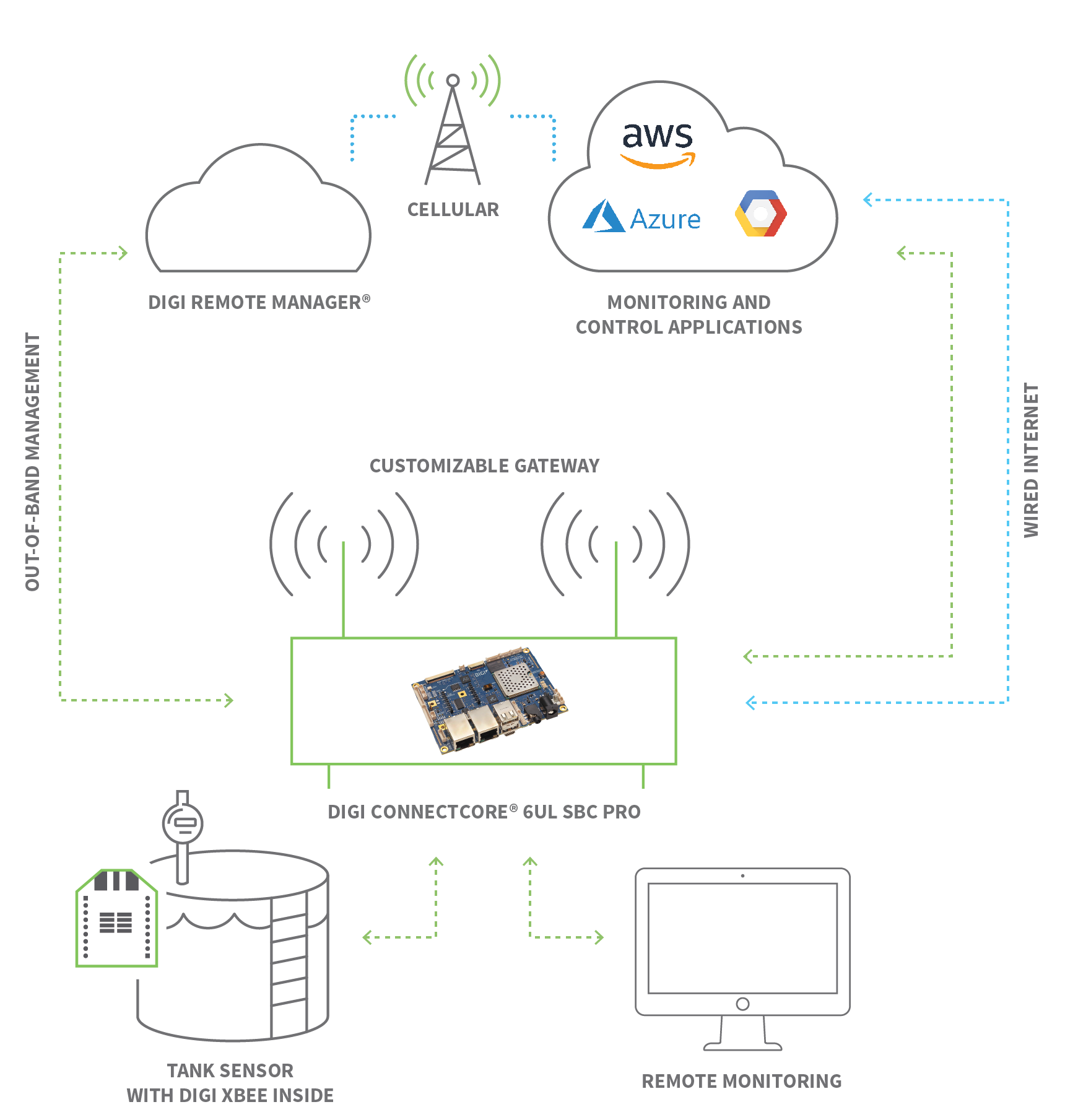
Socketxp is a cloud-based solution specifically designed for IoT remote access and device management. It provides secure SSH (Secure Shell) access to remotely located IoT devices, such as Raspberry Pi, Arduino, Nvidia Jetson, or any embedded Linux device situated behind a NAT router or firewall. Socketxp leverages secure SSL/TLS VPN tunnels to establish encrypted communication channels, ensuring that data transmitted between the user and the device remains protected from unauthorized access. This makes it an ideal solution for developers, engineers, and hobbyists who need to remotely manage and control their IoT devices securely.
Azure IoT Hub is another prominent platform for managing IoT devices in the cloud. It allows users to connect, monitor, and control millions of IoT devices securely and reliably. Azure IoT Hub provides a wide range of features, including device registration, authentication, command and control, and data ingestion. It also integrates with other Azure services, such as Azure Stream Analytics and Azure Machine Learning, enabling users to build comprehensive IoT solutions that can process and analyze device data in real time.
The process of controlling an IoT device remotely typically involves using a mobile app, web interface, or voice commands to interact with the device. When a user sends a command, it is transmitted over a network to the device, which then executes the desired action, such as turning on or off a light, adjusting the thermostat, or locking a door. The device then sends a confirmation message back to the user, indicating that the command has been successfully executed.
Consider the example of a smart thermostat. A user can remotely adjust the temperature settings of their home thermostat using a mobile app. The app sends a command to the thermostat, instructing it to increase or decrease the temperature. The thermostat then executes the command and sends a confirmation message back to the app. This allows the user to maintain a comfortable temperature in their home, even when they are away.
In the realm of industrial automation, remote device management plays a critical role in ensuring operational efficiency and safety. For instance, sensors embedded in machinery can transmit real-time data about temperature, pressure, and vibration. Engineers can remotely monitor this data to detect anomalies and predict potential equipment failures. If a problem is detected, they can remotely initiate maintenance procedures or shut down the equipment to prevent further damage.
Security is a paramount concern when it comes to remotely controllable IoT devices. Because these devices are connected to the internet, they are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the device's software or firmware to gain unauthorized access and control. This can lead to a variety of problems, including data breaches, device hijacking, and even physical harm.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to implement robust security measures. These measures include using strong passwords, keeping device software up to date, encrypting data transmissions, and implementing access control policies. It is also important to choose IoT devices from reputable manufacturers who prioritize security and regularly release security updates. Additionally, network segmentation can isolate IoT devices from critical network infrastructure, limiting the potential impact of a security breach.
The benefits of remotely controllable IoT devices are numerous. They provide increased convenience, improved efficiency, and enhanced safety. They enable users to manage their environments from anywhere in the world, optimize resource allocation, and prevent costly equipment failures. However, it is important to be aware of the security risks associated with these devices and to take appropriate measures to mitigate those risks.
The development and deployment of remotely controllable IoT devices are continuously evolving. As technology advances, new and innovative applications are emerging. From smart cities that optimize traffic flow and energy consumption to personalized healthcare solutions that monitor patient health and deliver remote treatment, the potential of IoT is vast. As the cost of sensors and processing power continues to decrease, and as network connectivity becomes more ubiquitous, we can expect to see even more widespread adoption of remotely controllable IoT devices in the years to come.
One of the key trends in IoT is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI and ML algorithms can analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices to identify patterns, predict trends, and automate decision-making. For example, AI-powered smart thermostats can learn a user's preferences and automatically adjust the temperature settings to maximize energy savings and comfort. Similarly, AI-driven predictive maintenance systems can analyze sensor data to predict when a machine is likely to fail, allowing maintenance to be performed proactively, thus preventing costly downtime.
Another important trend is the growing focus on interoperability. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, it is essential that these devices can communicate and interact with each other seamlessly. This requires the development of open standards and protocols that enable devices from different manufacturers to work together. Efforts are underway to develop such standards, and progress is being made in this area.
The future of remotely controllable IoT devices is bright. As technology continues to evolve, these devices will become even more sophisticated, capable, and secure. They will play an increasingly important role in our lives, transforming the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
Understanding IoT remote device management is crucial for anyone involved in deploying, managing, or using IoT devices. Essentially, it is the ability to control and monitor remote IoT access devices from a distance. This capability is transforming industries, enabling new business models, and enhancing user experiences.
In the context of smart homes, remote device management allows homeowners to control lighting, temperature, security systems, and appliances from anywhere with an internet connection. This not only provides convenience but also enhances security and energy efficiency. For example, a homeowner can remotely turn off lights left on accidentally, adjust the thermostat to save energy, or monitor security cameras while on vacation.
In industrial settings, remote device management is even more critical. It enables companies to monitor and control equipment, track inventory, and manage logistics from a central location. This improves operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and enhances safety. For example, a manufacturing plant can remotely monitor the performance of its machinery, detect potential problems, and initiate maintenance procedures before a breakdown occurs.
The key to effective IoT remote device management is a robust and secure infrastructure. This includes reliable network connectivity, secure communication protocols, and a centralized management platform. The platform should provide features such as device registration, authentication, configuration, monitoring, and control. It should also provide tools for managing security, such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, and access control.
One of the challenges of IoT remote device management is the diversity of devices and protocols. IoT devices come in all shapes and sizes, and they use a variety of communication protocols. This makes it difficult to manage them all from a single platform. To address this challenge, many companies are adopting open standards and protocols, such as MQTT and CoAP. These standards provide a common language for IoT devices to communicate with each other and with management platforms.
Another challenge is security. IoT devices are often deployed in unsecured environments, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the device's software or firmware to gain unauthorized access and control. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to implement robust security measures, such as strong passwords, data encryption, and access control policies. It is also important to keep device software up to date with the latest security patches.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of IoT remote device management are significant. It enables companies to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety. It also enables new business models, such as remote monitoring and maintenance services. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, the importance of remote device management will only increase.
In conclusion, the ability to remotely control and monitor IoT devices is a transformative technology that is reshaping industries and enhancing our daily lives. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT is enabling new levels of convenience, efficiency, and safety. However, it is essential to be aware of the security risks associated with these devices and to take appropriate measures to mitigate those risks. By implementing robust security measures and adopting open standards and protocols, we can harness the full potential of IoT and create a more connected, efficient, and secure world.
The continuous evolution of IoT technologies promises an even more interconnected future, where devices seamlessly communicate and collaborate to optimize our environments and enhance our experiences. As we move forward, it is crucial to prioritize security, interoperability, and user privacy to ensure that the benefits of IoT are realized responsibly and ethically.
Article Recommendations
- Diva Flawless Search Check Spelling More Tips Here
- Discover Melanies Story From Search Errors To Inspiring Life

Detail Author:
- Name : Prof. Darian Cassin
- Username : mante.myrl
- Email : pollich.corrine@bergnaum.org
- Birthdate : 2007-05-20
- Address : 13968 Kyle Path Suite 291 Arielleview, AK 08708-0745
- Phone : 612-209-3879
- Company : Buckridge Ltd
- Job : Transportation Equipment Maintenance
- Bio : Cum dolorem qui quia inventore. Ratione error accusamus rem ducimus et quis. Ad et quibusdam nostrum recusandae deleniti qui. Quis quia enim alias blanditiis illum eum.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/schummd
- username : schummd
- bio : Esse totam et voluptatem. Aliquam delectus perferendis quod est iste veritatis nostrum. Ut quis consequuntur velit excepturi voluptas.
- followers : 1768
- following : 105
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@dayna_schumm
- username : dayna_schumm
- bio : Aut consequatur ducimus voluptas quibusdam.
- followers : 1452
- following : 861
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/dayna_schumm
- username : dayna_schumm
- bio : Corporis sit similique quia at et. Libero consectetur saepe reprehenderit dolorem qui sint.
- followers : 5086
- following : 774
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/dschumm
- username : dschumm
- bio : Et enim quam maxime sint fuga quo voluptatem.
- followers : 1486
- following : 2653
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/schummd
- username : schummd
- bio : Sunt reiciendis distinctio repellendus ut vel qui est.
- followers : 3437
- following : 544