Royal Succession: Understanding Heirs To A Crown (Explained!)
Ever dreamt of ascending to a throne, bypassing the common routes of merit and achievement? The path to becoming an heir to a crown family is paved with centuries of tradition, complex legal frameworks, and, let's be honest, a considerable dose of luck. It's a world where birthright often trumps all, and understanding the nuances of succession is key.
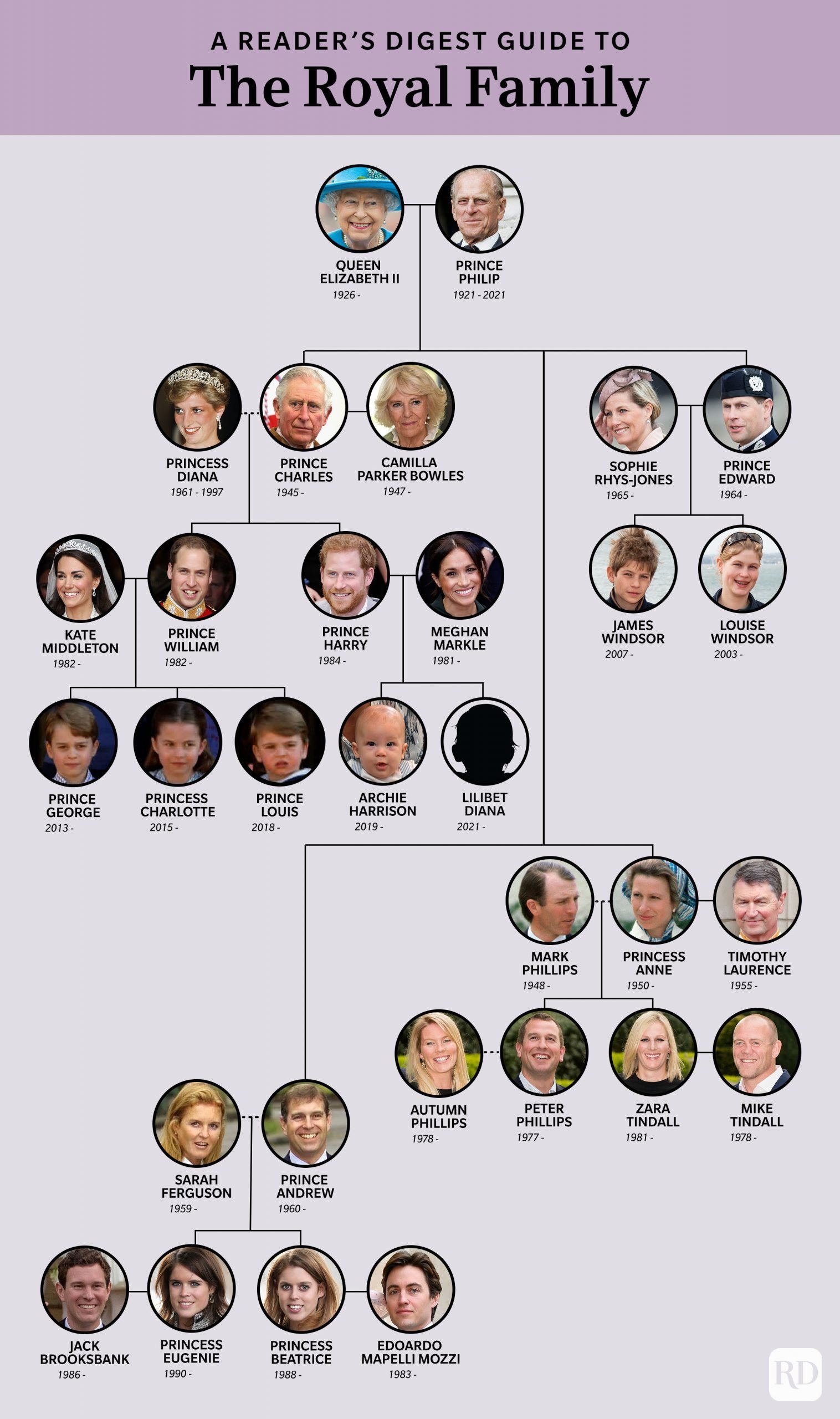
The allure of royalty is timeless, captivating imaginations with tales of opulent castles, ceremonial grandeur, and inherited power. While the idea of actively "becoming" an heir to a crown family might seem like a fanciful notion straight out of a fairytale, a closer examination reveals a fascinating tapestry of historical precedents, evolving legal codes, and the ever-present drama of dynastic ambition. Succession to a throne is not merely about lineage; it is a complex interplay of laws, customs, and political maneuvering that shapes the destiny of nations.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Concept | Heir to a Crown Family |
| Definition | An individual who is in line to inherit a throne or royal title, typically based on birthright and succession laws. |
| Governing Factors | Laws of succession (e.g., primogeniture, male-preference primogeniture, absolute primogeniture), royal decrees, political considerations, and historical precedents. |
| Key Elements | Lineage, legal frameworks, tradition, and political influence. |
| Primary Requirement | Biological relationship to the reigning monarch or a previous monarch within the established rules of succession. |
| Changing Dynamics | Modern succession laws are evolving to remove gender bias and prioritize equality. |
| Succession Act 2013 (UK) | Removed male preference, allowing the eldest child (regardless of gender) to become the heir apparent. |
| Historical Context | Historically, many monarchies favored male heirs to maintain power and military strength. |
| Role of the Monarch | The reigning monarch often has the authority to influence or change succession laws, subject to legal and political constraints. |
| Challenges | Succession crises can arise due to unexpected deaths, disputed claims, or political instability. |
| Royal Titles | Titles such as Prince/Princess of Wales, Crown Prince/Princess are often given to the heir apparent. |
| Becoming an Heir | It is primarily determined by birthright, but can sometimes be influenced by adoption or designation (subject to legal and political approval). |
| Political Factors | Public opinion, political alliances, and the stability of the monarchy play significant roles in succession. |
| Royal Family | The dynamics and relationships within the royal family can greatly affect the perception and acceptance of the heir. |
| Succession Examples |
|
| Reference | Official Website of the British Royal Family |
Article Recommendations
- Melissa Rauch Night Court Behind The Scenes More
- Maddi Pann Leak Privacy Concerns Weightlifting Talk Details


Detail Author:
- Name : Vaughn Greenholt
- Username : nicolette.dooley
- Email : parker.wolf@brown.com
- Birthdate : 1971-05-02
- Address : 3555 Cody Cape Suite 648 East Michael, OK 28981-0864
- Phone : 669.434.3682
- Company : Champlin-Bernier
- Job : Construction Equipment Operator
- Bio : Quos occaecati nemo nisi nihil enim. Et explicabo quos facilis nihil. Perspiciatis odio praesentium autem expedita explicabo magni quia. Quis modi voluptatum ut quibusdam quisquam et sunt.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/caylagibson
- username : caylagibson
- bio : Et harum ut aperiam ut qui qui voluptatem. At vero praesentium iusto nesciunt magnam earum.
- followers : 2660
- following : 1797
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@cayla_gibson
- username : cayla_gibson
- bio : Officiis nihil quo dolore saepe quod et corrupti inventore.
- followers : 3205
- following : 2515
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/gibson1970
- username : gibson1970
- bio : Et qui sunt facere possimus qui praesentium. In velit et illum quasi adipisci. Totam aut rerum laborum.
- followers : 2811
- following : 177
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/cayla.gibson
- username : cayla.gibson
- bio : Facere provident ut non iste dicta qui nesciunt.
- followers : 2051
- following : 1374